Plastic Surgery,
Liposuction and BBL by
Expert Cosmetic Surgeon
Los Angeles, CA
Specializing in Liposuction, Tummy Tuck, Breast Augmentation & BBL
Why Schedule a Consultation with Cosmetic Surgeon Dr. Moein?
Welcome to Moein Surgical Arts, where your journey to confidence and empowerment begins with Dr. Moein. With a genuine commitment to understanding your unique needs, Dr. Moein crafts personalized aesthetic treatment plans designed to enhance your natural beauty.
By scheduling a consultation, you’re taking an important step toward self-improvement and embracing body positivity. Dr. Moein's approach goes beyond aesthetic transformation; he aims to harmonize your vibrant spirit with your physical appearance. As a leading cosmetic surgeon, he is dedicated to demystifying every aspect of your desired procedures, ensuring you feel informed and comfortable every step of the way.
Start your journey with Dr. Moein today and discover the possibilities that await you!
SCHEDULE YOUR CONSULTATION TO:
- Meet with a Double Board-Certified Surgeon
Benefit from Dr. Moein's 20 years of specialized expertise - Receive a Comprehensive Surgical Evaluation
In-depth consultation including candidacy assessment and personalized treatment planning - Access Advanced Surgical Technology
Learn how Dr. Moein utilizes cutting-edge techniques including HD VASER and Renuvion skin tightening - Experience Direct Physician Care
Dr. Moein personally performs your surgery and remains accessible 24/7 throughout your recovery - Understand Your Complete Care Package
All-inclusive pricing covers pre-operative preparation, surgery, and post-operative care - Explore Flexible Investment Options
Multiple financing solutions available to qualified patients, including 0% interest programs
DR. BABAK MOEIN, MD FACS RENOWNED LOS ANGELES PLASTIC SURGERY

Dr. Babak Moein, MD, FACS, is a renowned LA cosmetic surgeon and one of the top-ranked liposuction surgeons in Los Angeles. Board-certified and fellowship-trained, Dr. Moein combines advanced surgical skill with the latest technologies, including VASER liposuction and Renuvion skin tightening, to help patients achieve exceptional body contouring results.

Dr. Moein is board certified by the American Board of General Surgery (2005 – Re-certified in 2025).
LA cosmetic surgeon Dr. Moein has a long career helping men and women achieve their body goals in Los Angeles, CA. With over 20+ years of experience following extensive surgical training, Dr. Moein is the aesthetic surgeon to help you with all your aesthetic goals. From cosmetic procedures to minimally invasive surgeries, Dr. Moein has the know-how to give you the body or skin of your dreams, about LA cosmetic surgeon Dr. Moein in Los Angeles CA.








Cosmetic Patient Success Stories


BODY CONTOURING
LA cosmetic surgeon Dr. Moein specializes in today's most advanced surgical and non-surgical procedures. Dr. Moein of Moein Surgical Arts combines years of experience and cutting-edge technology to give you the body you want with fat-busting procedures like VASER lipo or a full-on tummy tuck. Tired of that belly fat that won’t budge or those love handles that you no longer love? See Dr. Moein for a complimentary consultation in Los Angeles, CA. Virtual appointments are available too.
LIPOSUCTION
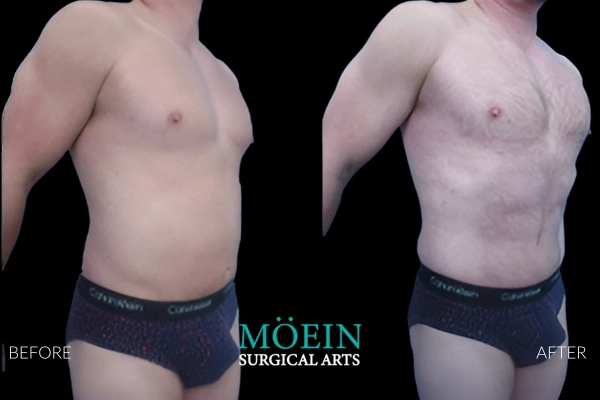
Liposuction removes excess and stubborn
fat from problem areas and contours the body to achieve the desired aesthetic. At Moein Surgical Arts
This cosmetic treatment is customized based on the patient’s ideal goals. We can even relocate healthy fat for a BBL.
Vaser Liposuction
Vaser Liposuction is an advanced cosmetic procedure utilizing ultrasound technology to selectively target and break down fat cells. This minimally invasive technique allows for precise sculpting, promoting smoother results and quicker recovery compared to traditional liposuction. Vaser Liposuction effectively contours various body areas, providing a refined silhouette.
MOMMY MAKEOVER
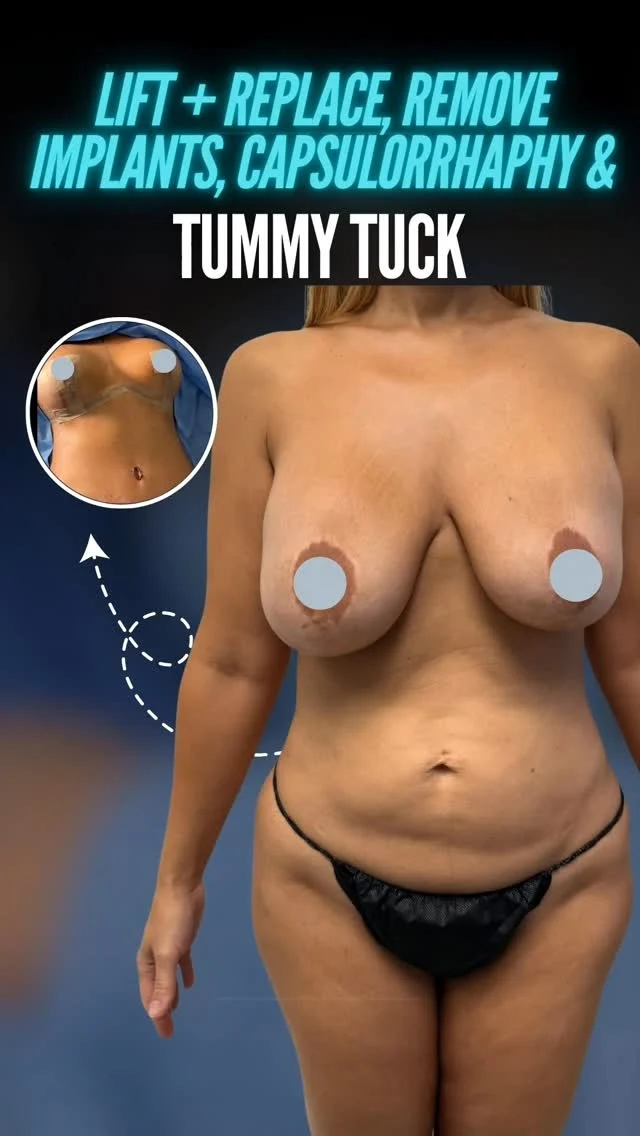
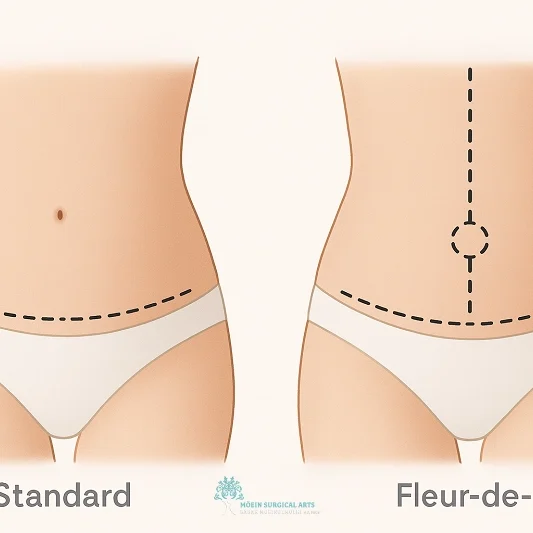
A Tummy Tuck, or abdominoplasty, is a surgical procedure that removes excess skin and fat from the abdominal area. It tightens weakened muscles, creating a firmer, more contoured midsection. This transformative surgery is ideal for individuals seeking to achieve a flatter stomach and improved abdominal tone.
Tummy Tuck- Abdominoplasty
A Tummy Tuck, or abdominoplasty, is a surgical procedure that removes excess skin and fat from the abdominal area. It tightens weakened muscles, creating a firmer, more contoured midsection. This transformative surgery is ideal for individuals seeking to achieve a flatter stomach and improved abdominal tone.
HD LIPOSUCTION
High-Definition Liposuction (HD Lipo) is an advanced body contouring technique that precisely targets and sculpts localized fat deposits. Using specialized tools, surgeons define muscle groups, revealing a more toned and sculpted appearance. This minimally invasive procedure enhances body contours with minimal downtime, providing natural-looking results.
Body Lift
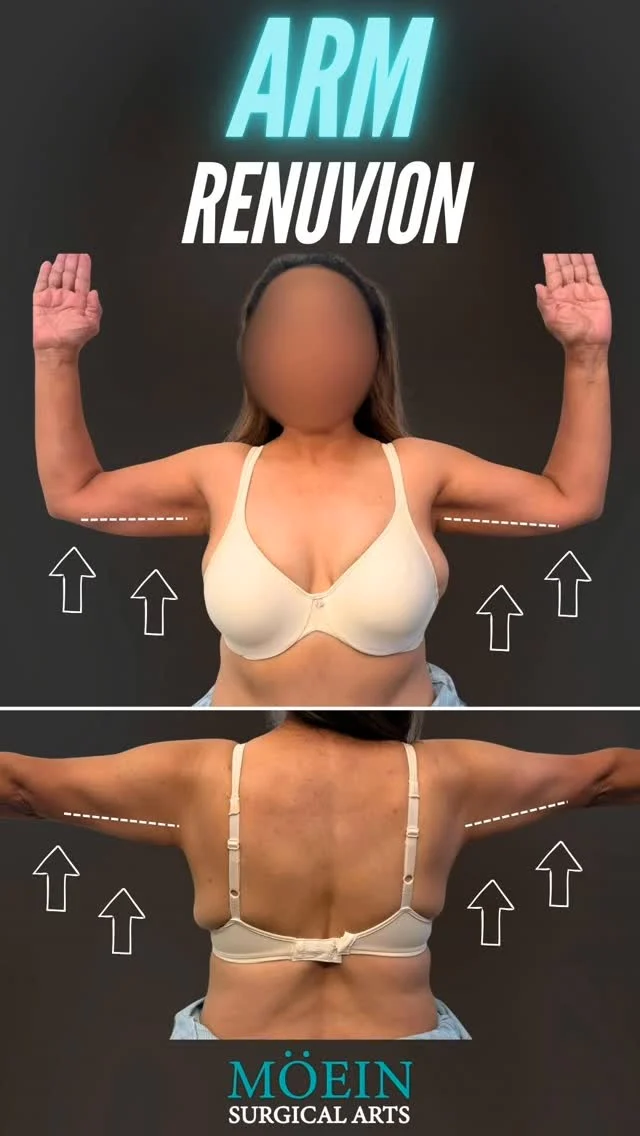
RENUVION
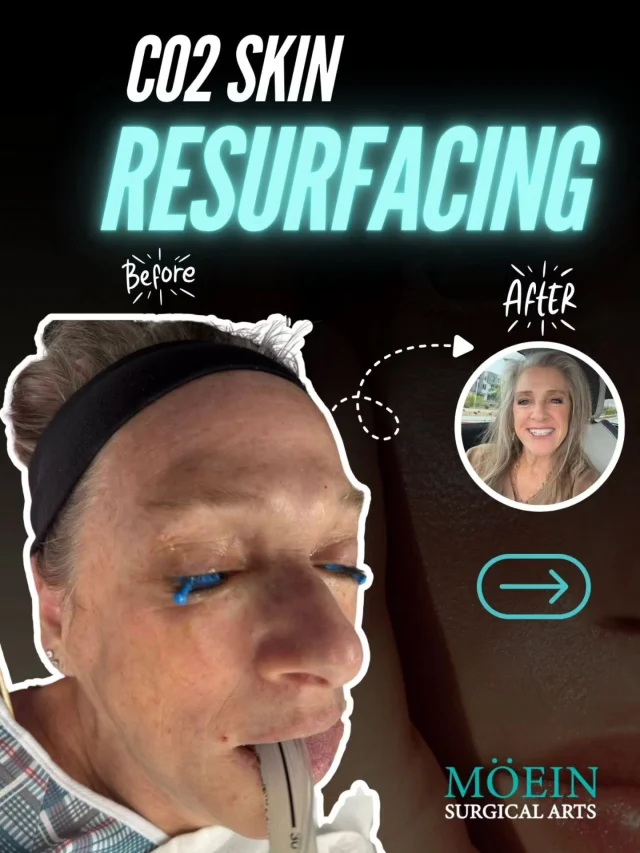
RENUVION is an innovative cosmetic technology combining radiofrequency energy and helium plasma to tighten and rejuvenate skin. Used in various procedures like skin resurfacing and body contouring, RENUVION promotes collagen production, resulting in firmer and smoother skin. This minimally invasive technique offers effective skin tightening with reduced downtime and scarring.
AB ETCHING
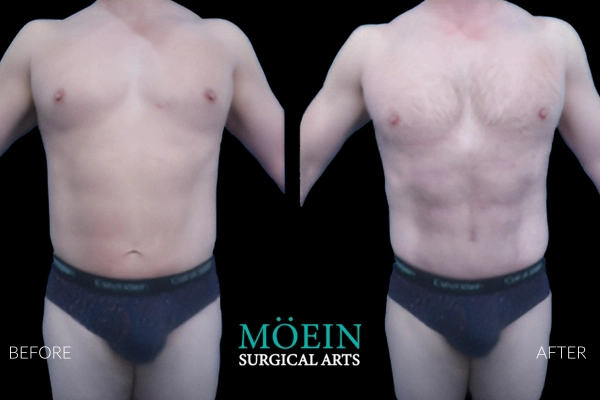
Abdominal etching, or AB ETCHING, is a cosmetic surgery technique that sculpts the appearance of well-defined abdominal muscles. Through liposuction, fat deposits are strategically removed, emphasizing the natural contours of the abdominal muscles. This procedure provides a more sculpted and athletic look, enhancing the definition of the abdominal area.
BRAZILIAN BUTT LIFT
A butt augmentation can be achieved
surgically and nonsurgically with butt
implants or a Brazilian butt lift
procedure in Los Angeles, CA. Enhance
the size and shape of the buttocks with
a butt augmentation procedure.
THIGH LIFT
A thigh lift is a surgical procedure that contours and tightens the thighs by removing excess skin and fat. Ideal for addressing sagging skin due to aging, weight loss, or genetics, the surgery results in smoother, more sculpted thighs. Thigh lifts enhance leg contours, providing a firmer and more youthful appearance.
POST-BARIATRIC BYPASS SCULPTING
Post-Bariatric Bypass Sculpting is a transformative procedure for individuals who have undergone significant weight loss. This comprehensive surgery addresses excess skin and fat, contouring the body for a more proportional and toned appearance. The sculpting process helps patients achieve their desired body shape, enhancing confidence and overall well-being.
Arm Lift
An arm lift, or brachioplasty, is a cosmetic surgery that removes excess skin and fat from the upper arms, resulting in a more toned and defined appearance. This procedure tightens sagging skin, addressing concerns related to weight loss or aging. Arm lift surgery enhances arm contours, promoting increased self-confidence.
BREAST SURGERY
BREAST AUGMENTATION
A breast augmentation can add volume
and shape to the breasts with breast
implants. Breast implants come in a variety
of shapes, textures, sizes, and types. Dr. Moein
a LA cosmetic surgeon is highly experienced
with breast augmentation procedures.
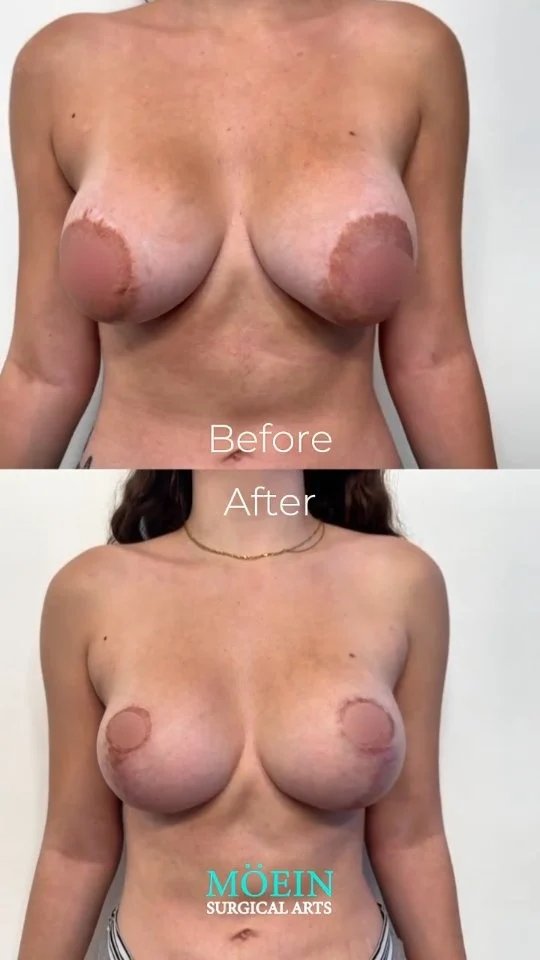
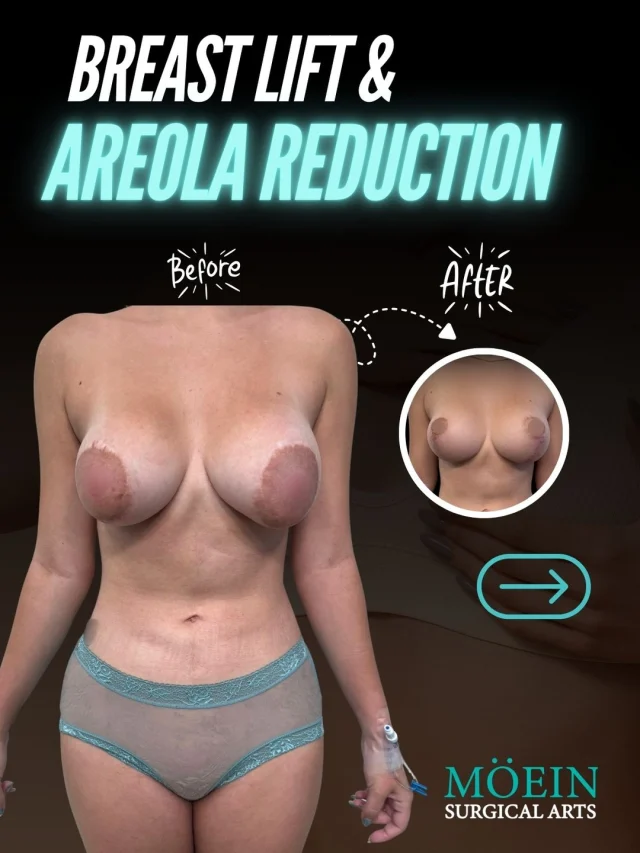
BREAST LIFT
A breast lift can remove the excess skin that
causes your breasts to sag. Your surgeon
carefully tightens the remaining tissue. The result
is a firmer, more youthful appearance. This
procedure reverses the effects of pregnancy,
genetics, and environmental factors.
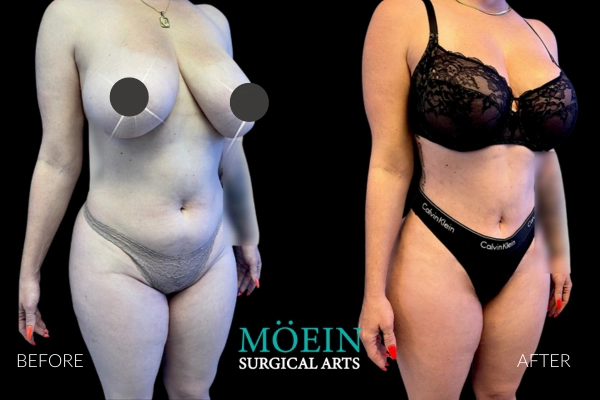
BREAST REDUCTION
Breast reduction, also known as a
reduction mammoplasty reduces
the size and weight of the breast.
This procedure is often combined with
a breast lift to achieve the desired
appearance.
FACE PLASTIC SURGERY
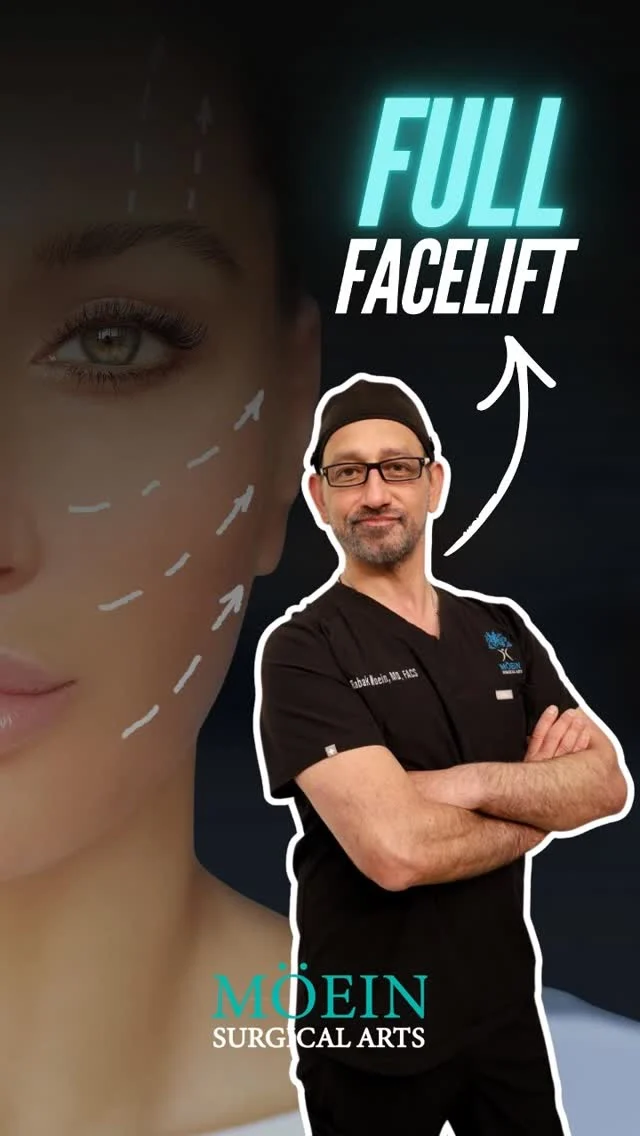
FACE LIFT
If you've reached the point where
you're bothered by sagging skin on your face, you can opt for a facelift rhytidectomy) to lift and tighten your skin for a more youthful appearance. This helps to reverse the signs of aging. A facelift can be performed by itself or in combination with another procedure. Visit LA cosmetic surgeon Dr. Moein for your facelift today.
NECK LIFT
A neck lift, or lower rhytidectomy, is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to improve the visible signs of aging in the jawline and neck. As we age, the skin in this area can lose elasticity, leading to sagging and excess fat deposits, resulting in an aged or tired appearance. A neck lift targets these issues by tightening the underlying muscles, removing excess skin, and sometimes redistributing or removing fat.
BROW LIFT
A brow lift, also known as a forehead lift, can erase signs of aging and rejuvenate the appearance. This procedure targets signs of aging in the brow and forehead area.
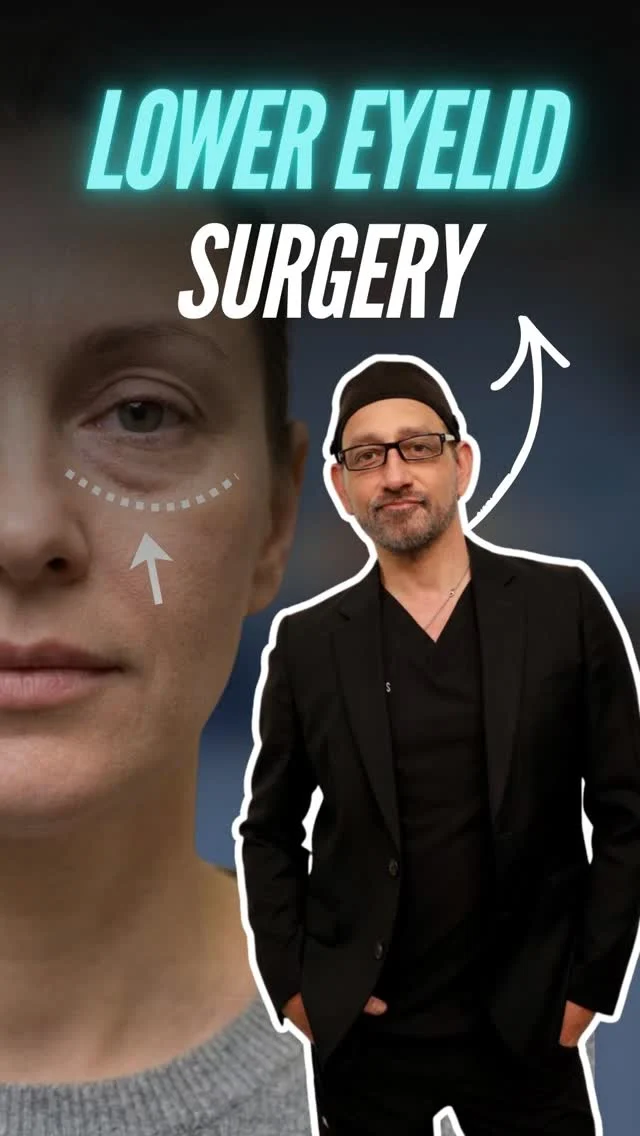
UPPER EYELID SURGERY
An upper lid blepharoplasty can be used to trim away excess drooping skin, tighten and alter muscles and embranes, and remove uneven deposits of fatty tissue.
COSMETIC SURGERY PATIENTS' RESULT
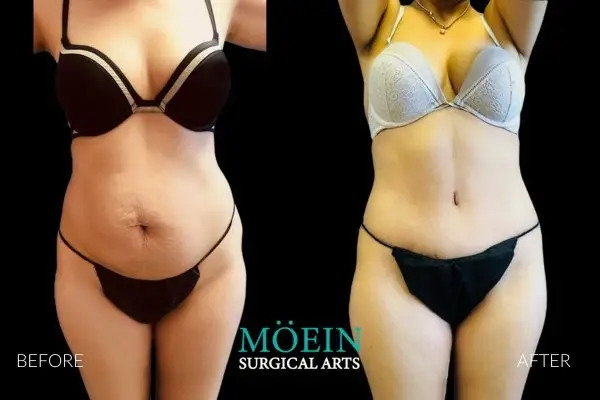
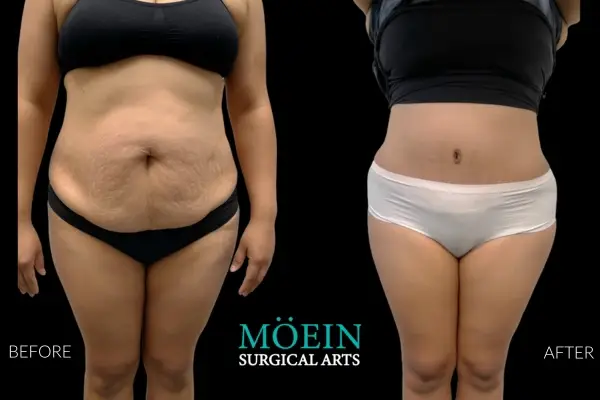
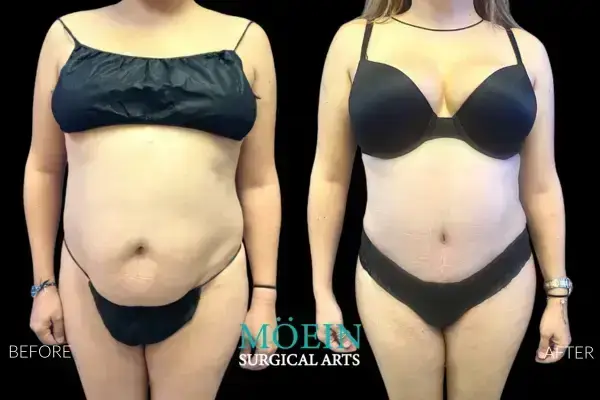
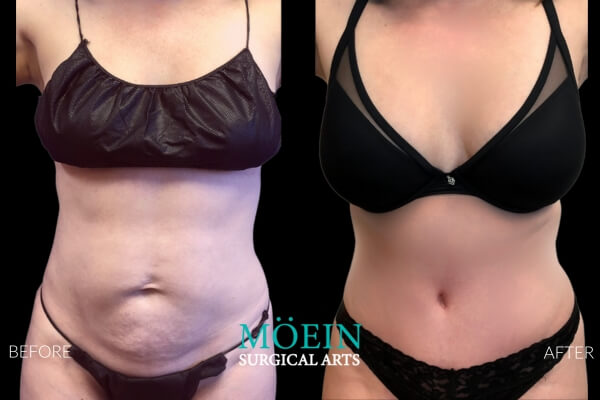
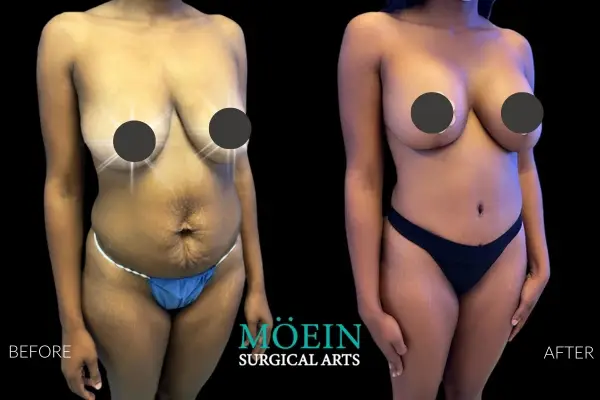
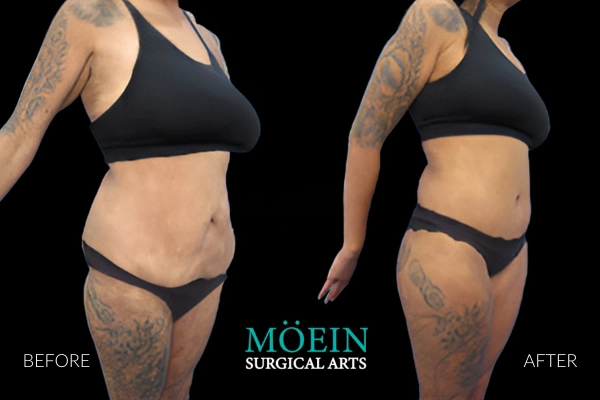
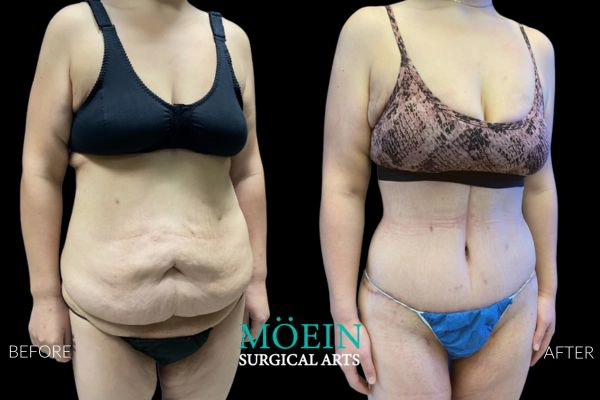
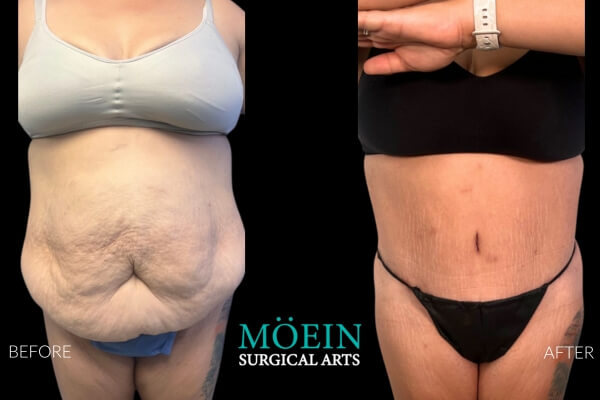
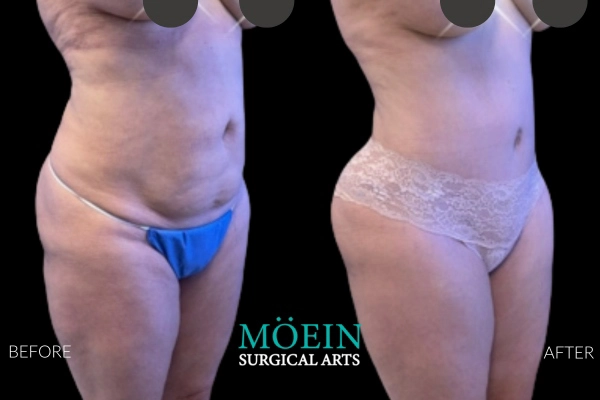
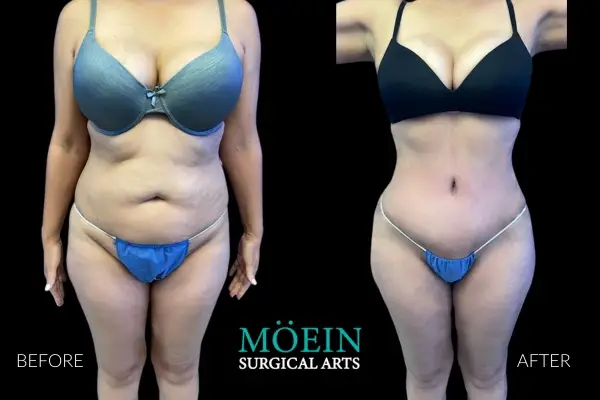
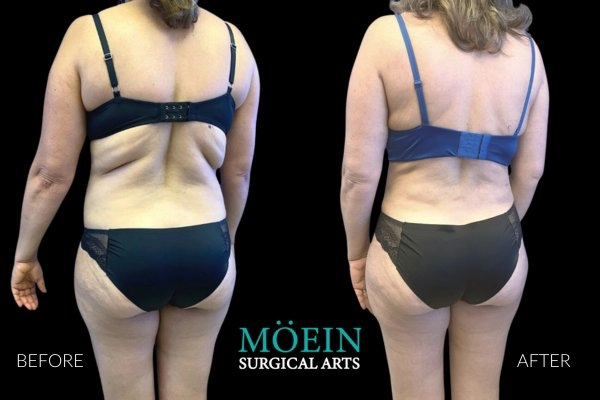
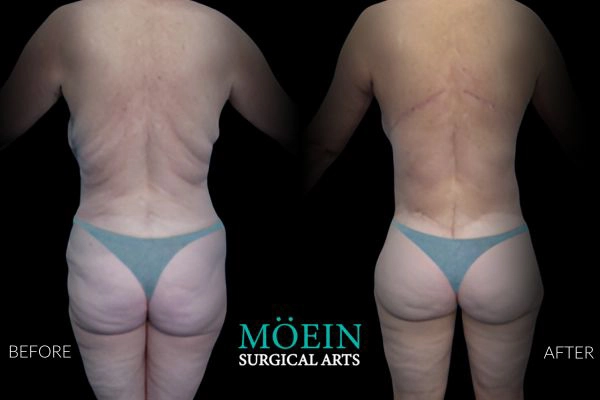
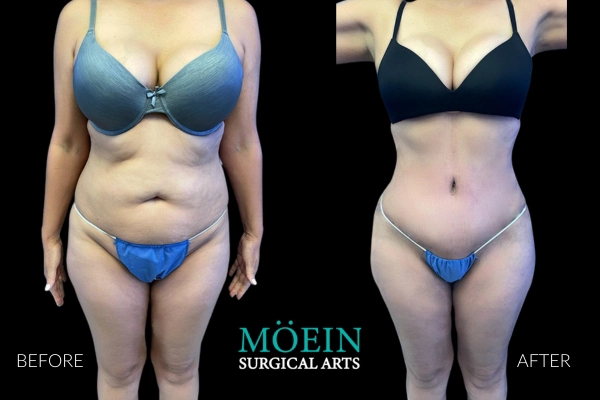
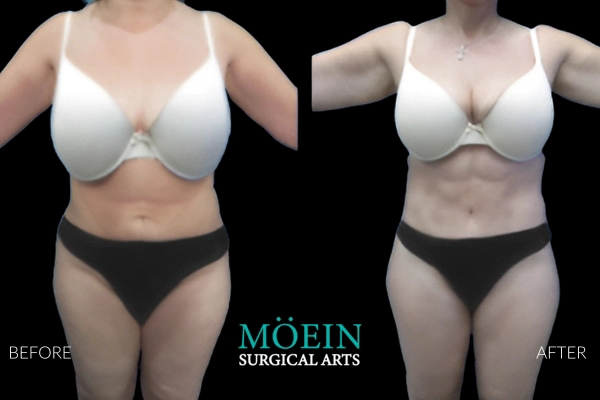
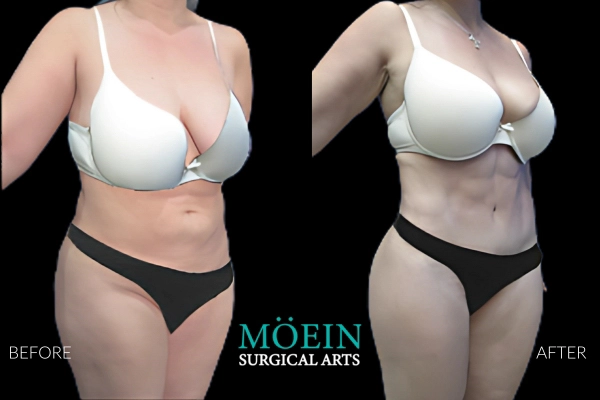
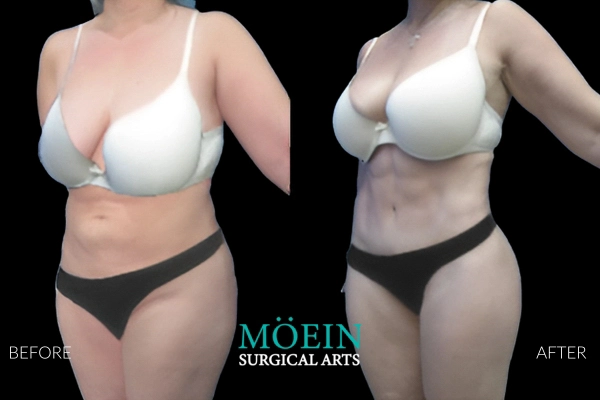
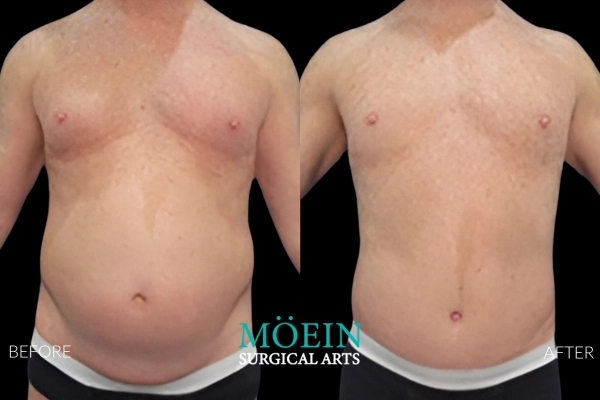
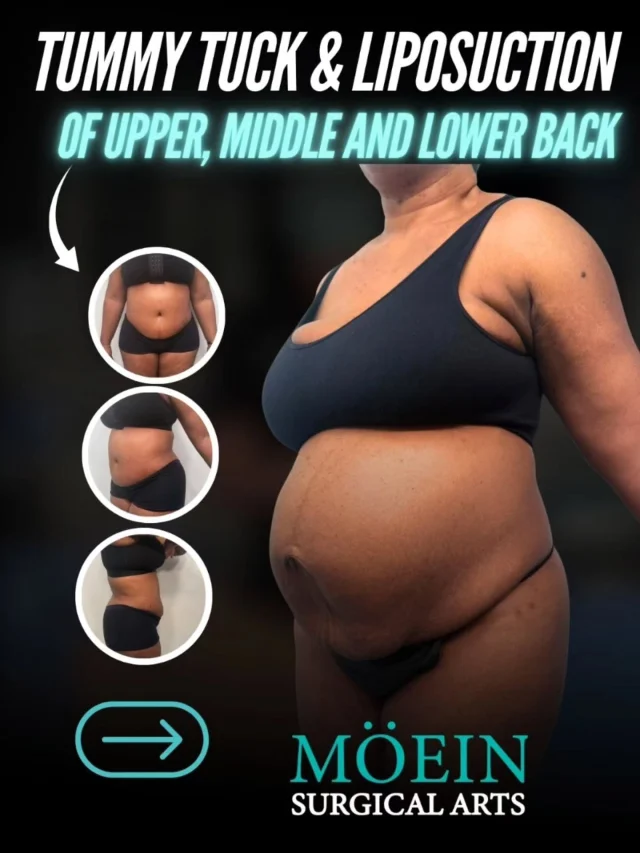
Tummy Tuck Before and After
Superior Tummy Tuck results are predicated on establishing 5 objectives using proprietary high-definition body contouring protocols. These objectives are demonstrated by our featured patients presented above and include:
- Aesthetically appropriate proportions with a concave upper and convex lower contour
- A belly button that is optimally positioned and shaped
- Exaggeration of waistline curve
- Avoidance of dog ears
- An incision line that is well hidden under your garments
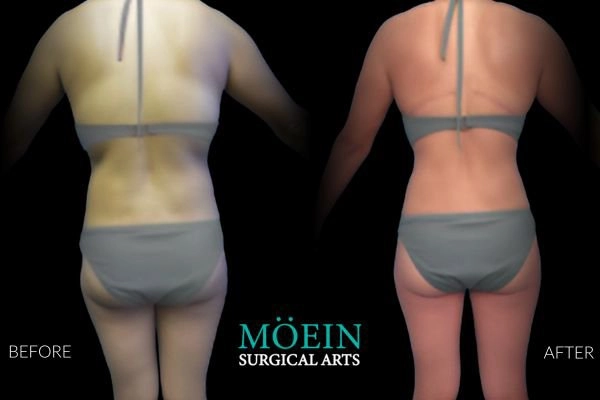
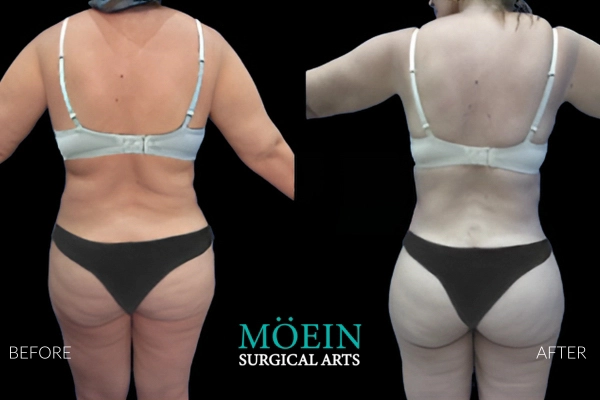
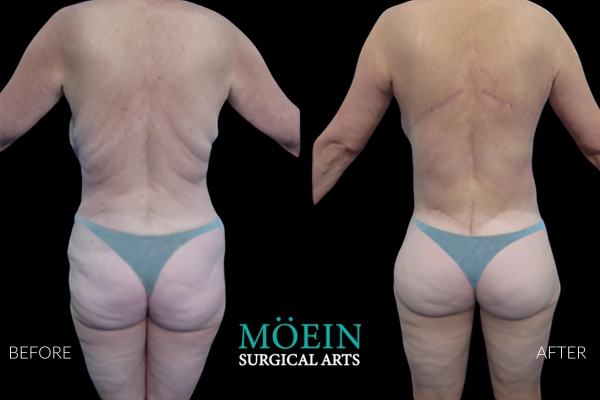
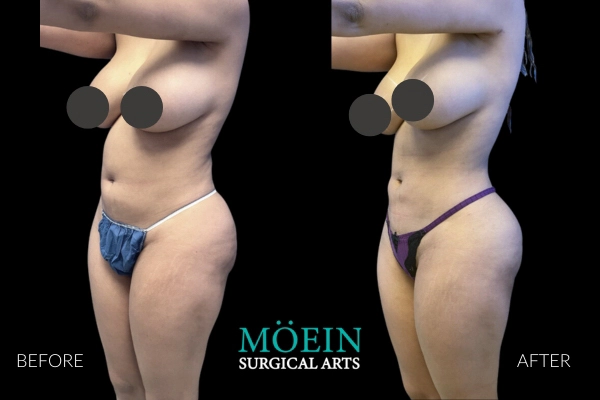
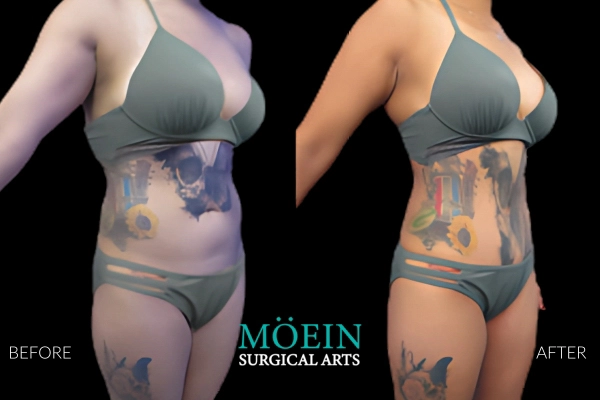
Back Liposuction Before and After
Optimized back liposuction requires both reduction of excess fat to achieve waistline narrowing and accommodation of skin redundancy to eliminate bra rolls as demonstrated by our featured patients. High-definition back contouring relies on the administration of state-of-the-art tools such as VASER liposuction and Renuvion J-plasma skin tightening.
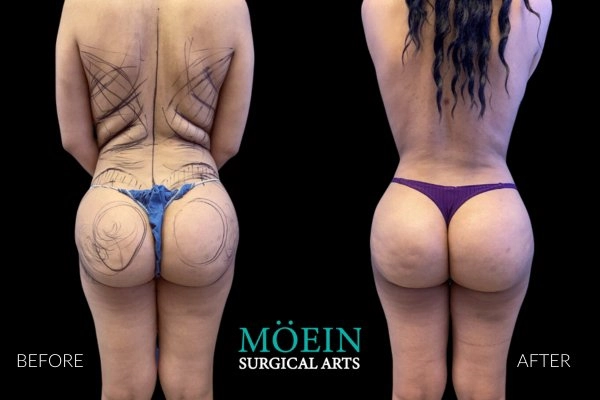
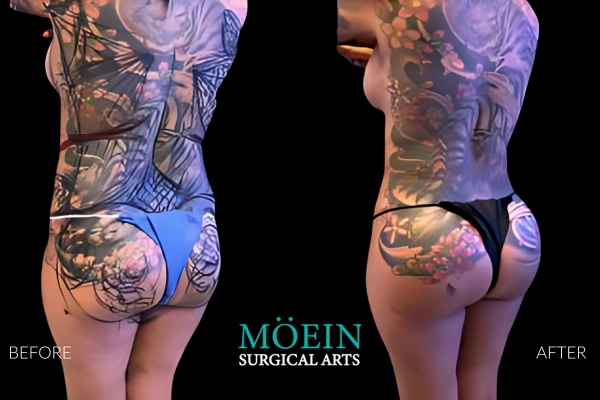
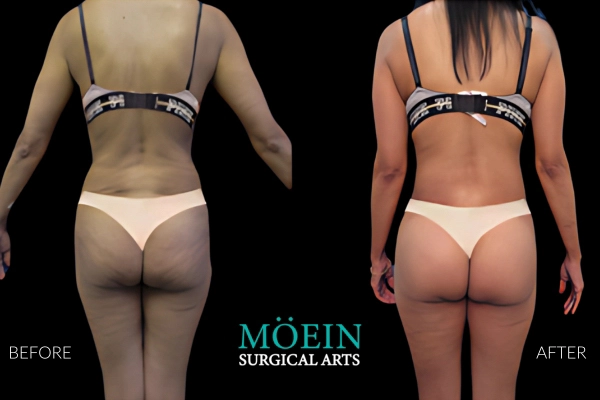
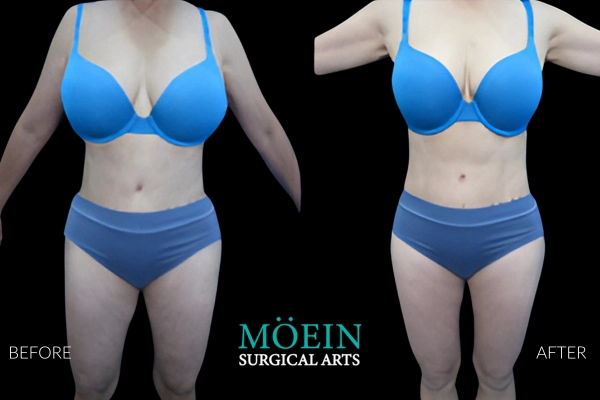
BBL Before and After
Successful Brazilian Buttock Lift outcomes are realized when the buttock shape and size created are customized to each patient’s unique desires. Our patients are provided the unique opportunity to communicate their specific buttock goals using our proprietary Brazilian Buttock Lift Assessment Tool.
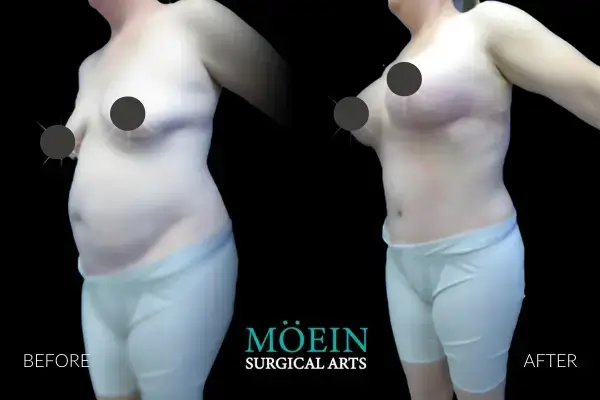
Liposuction of the abdomen is routinely performed at our center using both awake and general anesthesia depending on your preference. The scope of abdominal contouring ranges from subtle improvements of localized concern areas to creation of six packs by unveiling abdominal muscles using high definition protocols as demonstrated by our featured patients.
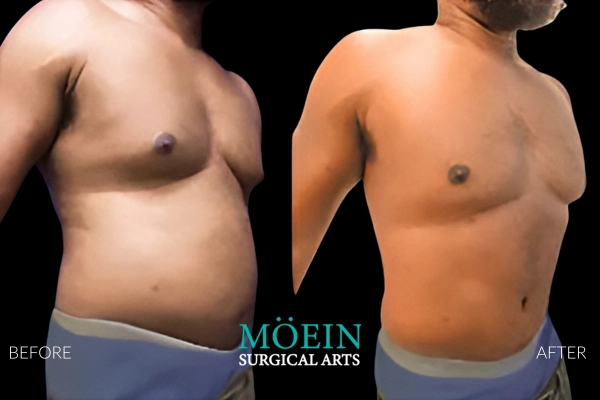
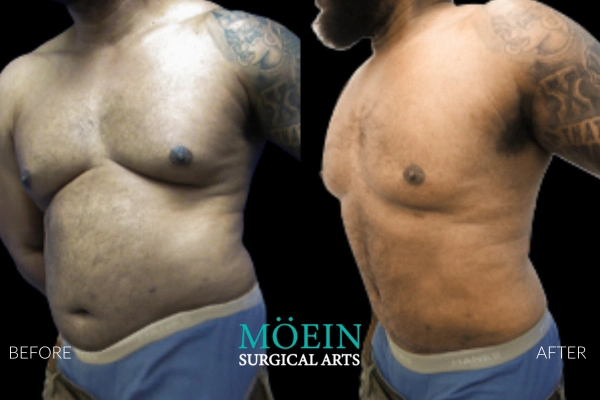
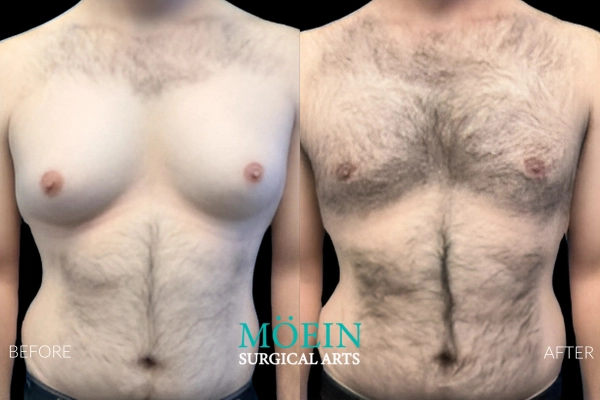
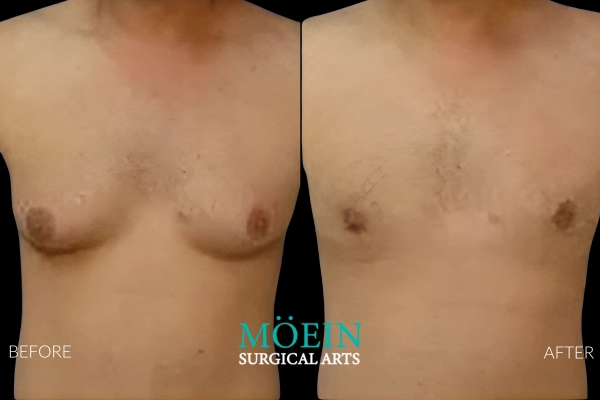
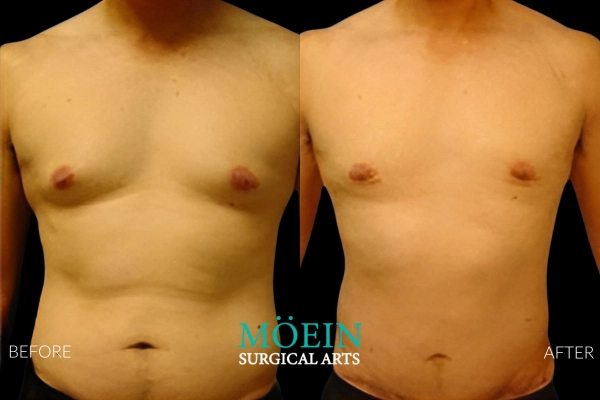
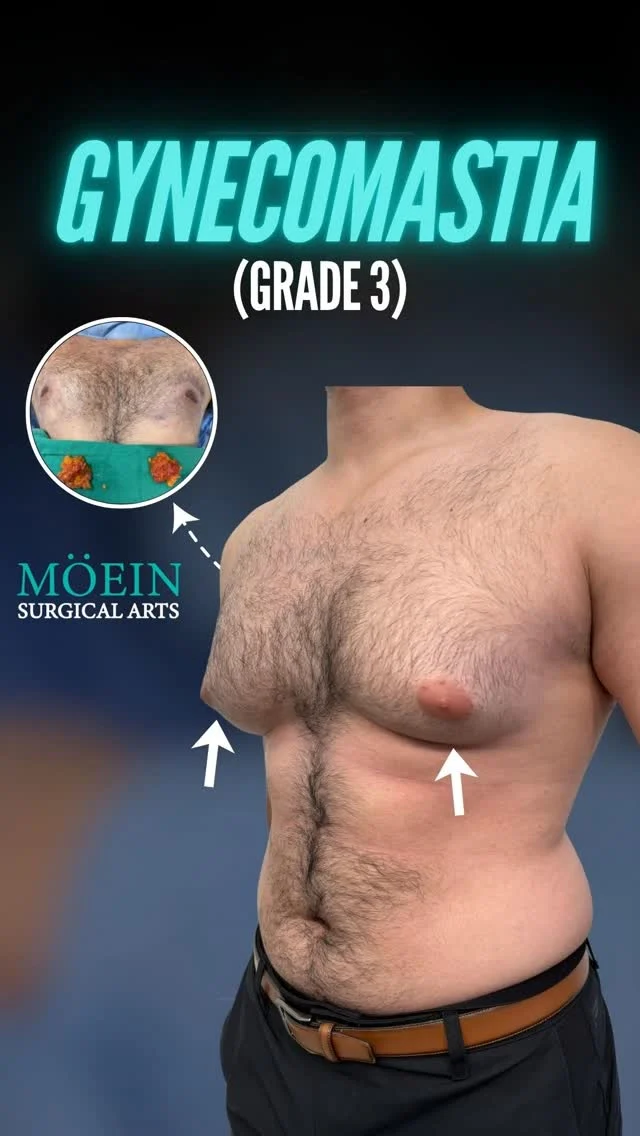
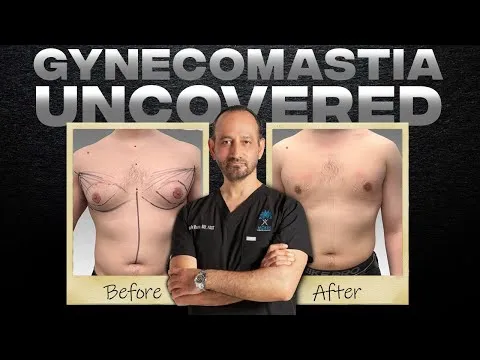
Gynecomastia Surgery Before and After
Gynecomastia describes the masculinization of the feminized chest that many male clients struggle with. Please appreciate the improvement in chest contours realized by our featured patients.
Male Breast Reduction Surgery Los Angeles
COSMETIC / PLASTIC SURGERY
LA cosmetic surgeon Dr. Moein specializes in minimally invasive surgery and cosmetic aesthetic and body contouring surgery. Moein Surgical Arts servers the greater LA area.
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY
Contour and sculpt the body with the leading surgical and non-surgical weight loss procedures at Moein Surgical Arts by a cosmetic surgeon in Los Angeles, CA.
MED SPA (FILLERS AND INJECTABLES)
Refresh your appearance and maintain a youthful glow with minimally invasive med spa services. Make age just a number at our medical spa.